Smart contracts are programs based on decentralized distributed ledger technologies (DLT) that are executed based on specific logic and agreements. Due to their characteristics, they can help reduce document forgery and increase accessibility, which is why there are a large number of applications.
Preservation and accessibility of documents
Forgery of certificates and documents has been a major problem faced by individuals and institutions for years. Physical and digital documents are prone to getting lost, and there is often no way to authenticate certificates quickly without contacting the issuer, which is a lengthy process.
Because it requires timely and secure authentication, smart contracts can help eliminate the complexities of the process by ensuring the authenticity of a certificate or document using the underlying distributed ledger technology (DLT) scanner. In this case, the certificate’s public key is scanned into the scanner and, since the DLT cannot be modified, the authenticity of the certificate can be trusted.
Distributed ledger technology also aids file retention and availability, as copies of the ledger are maintained on numerous servers, ensuring:
- Patents and copyrights are verifiable and infallible, as the timestamps of a smart contract cannot be modified.
- Files are easily accessed
- Documents exist on multiple computers in the network
- Document validity can be easily checked
Administrative payments and invoicing
Money transactions require high levels of trust and transparency, especially important for companies in industries that handle large volumes of financial transactions, such as insurance. When we consider existing traditional money management processes, such as escrow, for example, they can be susceptible to rare human interference.
Payroll in its current form for organizations operating in a global supply chain often lacks self-sustainability because the global banking system is complicated and it can be difficult to pay employees and manage transaction flows from different countries. This is because many countries operate different systems that generally require some form of transaction mediation process; this can be problematic in an increasingly remote first world where location is less of a factor in employment and business than ever before. In addition, other areas of use, such as national tax systems, may benefit as previously inefficient administrative and maintenance costs can be reduced.
Smart contracts provide solutions to these payment problems as they are transparent, secure and inexpensive to maintain. In addition, they have a long lifespan and can be easily automated to suit any payment need process in question, curbing mismanagement of funds.
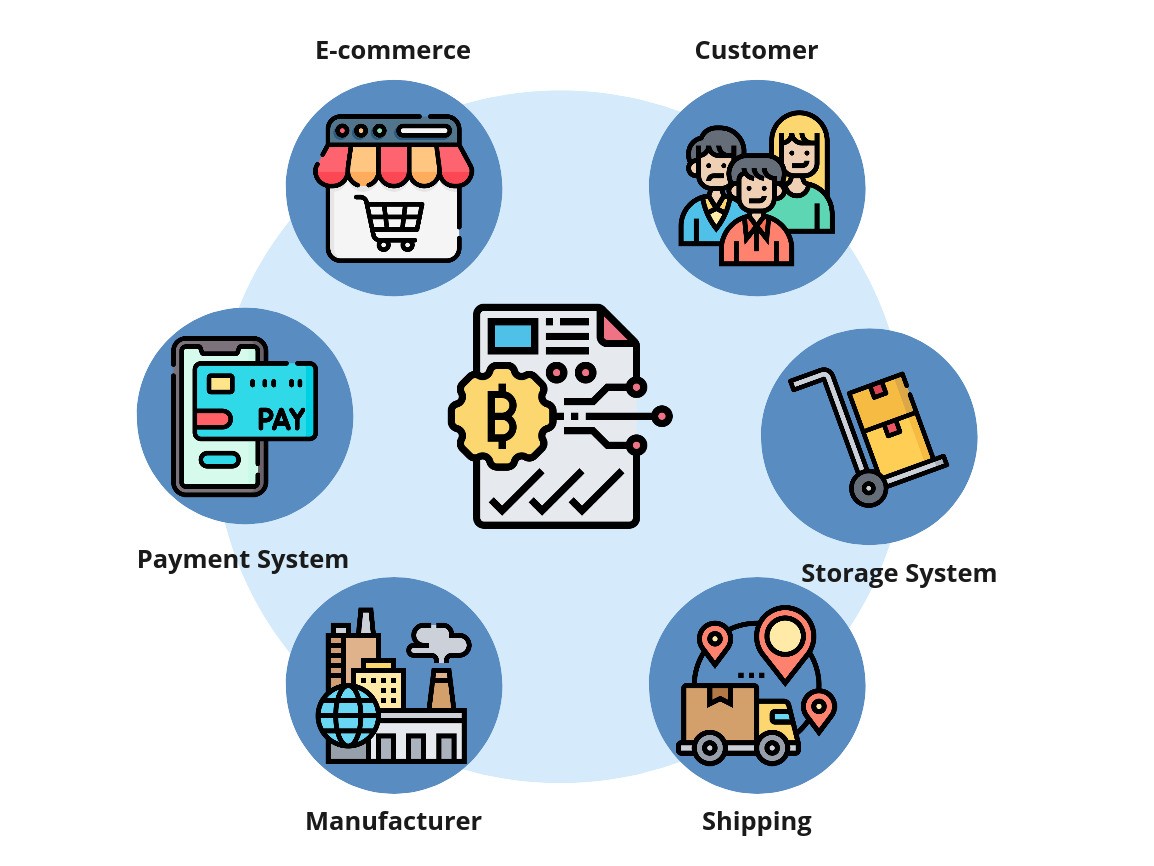
Supply chains
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations estimates that more than one-third of the world’s food is wasted, and this loss is estimated to be worth approximately $940 billion. They estimate that around 957 million people in 93 countries do not have enough to eat.
In the healthcare sector, there are numerous cases of wasted medicines and materials that could have found their way to other medical facilities, but due to the lack of a system to track what is available, they are not received.
Smart contracts could reduce, if not eradicate, waste of food and medical supplies, among others. An IoT smart contract can be written to assign public keys to packages whose data would exist in distributed registry technology, along with the location of the package and, if necessary, the medical facility that owns it. In this way, stakeholders can access their needs and we can find matches between markets and commodities more effectively to generate greater efficiencies.
A good use case for this type of smart contract would be a situation where different blood types are available in separate locations, but facilities lack the visibility to procure them. Thanks to smart contracts, it is possible to remedy this and allow greater flexibility within supply chains to respond effectively, meaning that:
- Proof of existence can be easily accessed.
- The location of a commodity can be tracked and updated seamlessly
- Matching is more accessible and can be done on a global scale
Real estate and crowdfunding
Crowdfunding opens up a wider range of opportunities when it comes to what can be raised with real-world assets, creating marketplaces that are easily accessible and offer a wider range of products than currently exist. Crowdfunding changes the way commodities are bought and sold and how funds can be raised for large projects.
Currently, if you are going to build a project and raise funds, this requires a lot of paperwork and time, both of which are increasingly valuable resources in a digitized world. However, using a smart contract for the same process is a matter of clicking a button and logging into a wallet. In addition, various parts of an asset can be tokenized so that different people can hold and own portions. They can sell them at any time in designated markets, just as we have seen the trading of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) skyrocket.
Properties, like real estate, can be sold online at any time without the lengthy process and paperwork involved in a smart contract. This is one of the many ways smart contracts create new market opportunities, provide flexibility and benefits such as:
- Ease of use
- Tokenization of more tangible assets
- Open and timeless markets
- Flexible global economy
Identity Management
Existing technologies used to prevent crimes such as identity theft are not as effective as they should be, as many of them do not give the owner full control over their data and the information they choose to provide.
Digital identifier smart contracts (DID) based on distributed (decentralized) registry technologies give individuals full control of their data and allow them to share the content of their data as they wish, which increases security, reduces the possibility of data mismanagement or a breach, and ensures:
- Identity security
- The user chooses the data he/she gives
- Easy KYC verification
Comparison of statistics
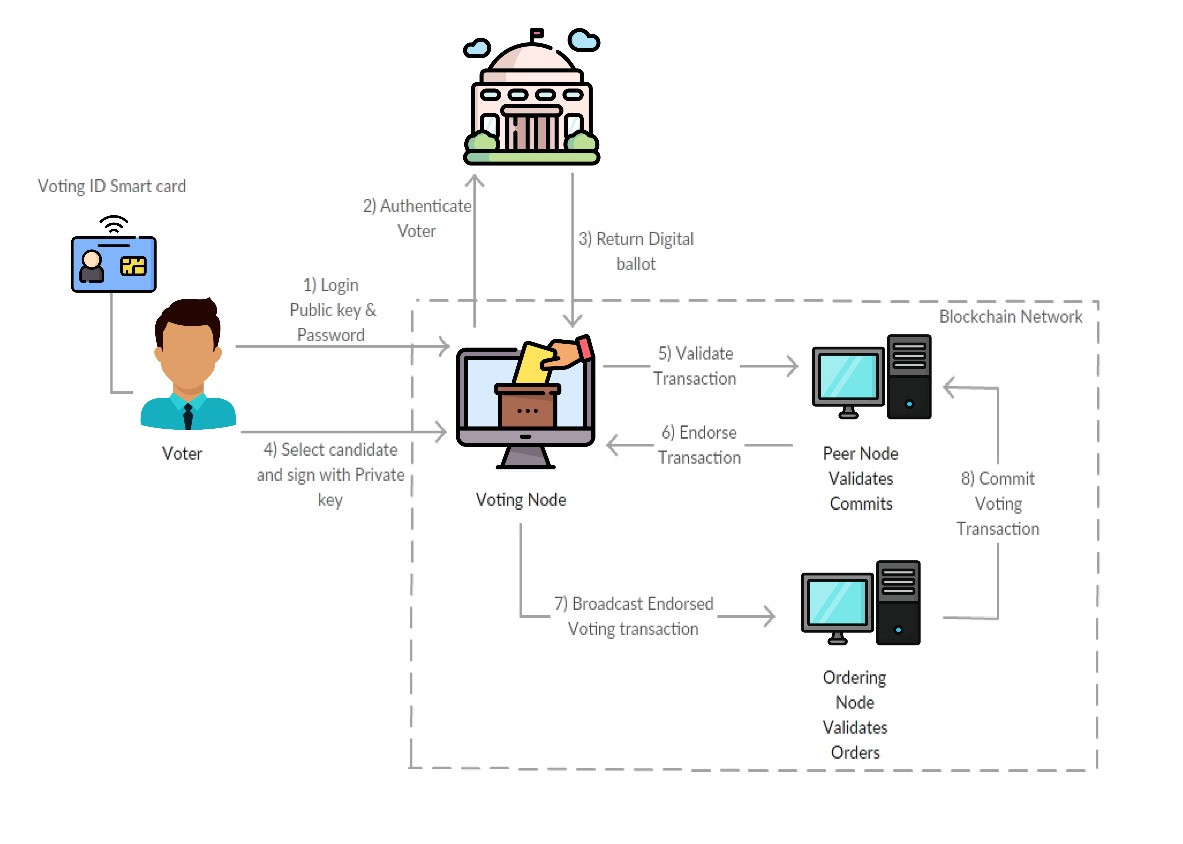
The decentralized and transparent nature of distributed registry technologies can be of great use in areas such as polls, particularly voting processes and other statistical collections.
Smart contracts for voting, population censuses and statistical collection help build confidence in the results, as no one person or organization can preside over the data collection and reading of the results: everyone can see the facts and figures for themselves. In addition, they can be programmed to feed the status of the process as they are activated; as a result, it is easier for users to accept and trust the process, bringing benefits such as:
- Improved accuracy of results.
- Reduced cost of elections.
- Reliable results due to the transparency of the process
- Fewer resources needed for data collection